Module common
This document contains technical documentation for the common module.
To browse the source code, visit the repository on GitHub.
This module contains a large collection of VHDL entities and packages that are useful in everyday FPGA design.
addr_pkg.vhd
Collection of types/functions for working with address decode/matching.
assign_last.vhd
Calculate the last indicator for an AXI-Stream-like handshaking data flow.
Can be used to enable packet-based processing from a data source that does not provide
a last signal.
The packet length is specified at compile-time using the packet_length_beats generic.
last will be asserted every packet_length_beats’th beat that passes.
This entity shall be instantiated in parallel with the data bus.
The ready and valid ports must be assigned combinatorially.
The last shall be assigned combinatorially alongside the ready and valid signals
that go towards the data sink.
Note
This entity also produces a first signal.
This is not part of the AXI-Stream specification, nor is it commonly used.
But it might be useful in some cases.
Feel free to ignore it.
attribute_pkg.vhd
Commonly used attributes for Xilinx Vivado, with description and their valid values. Information gathered from documents UG901 and UG912.
axi_stream_protocol_checker.vhd
Check that an AXI-Stream-like handshaking bus is compliant with the AXI-Stream standard. Will perform the following checks at each rising clock edge:
The handshake signals
readyandvalidmust be well-defined (not'X','-', etc).validmust not fall without a transaction (ready and valid).No payload on the bus may change while
validis asserted, unless there is a transaction.strobemust be well-defined whenvalidis asserted.
If any rule violation is detected, an assertion will be triggered.
Use the logger_name_suffix generic to customize the error message.
Note
This entity can be instantiated in simulation code as well as in synthesis code. The code is simple and will be stripped by synthesis. Can be useful to check the behavior of a stream that is deep in a hierarchy.
Comparison to VUnit checker
This entity was created as a lightweight and synthesizable alternative to the VUnit AXI-Stream
protocol checker (axi_stream_protocol_checker.vhd).
The VUnit checker is clearly more powerful and has more features, but it also consumes a lot more
CPU cycles when simulating.
One testbench in this project that uses five protocol checkers decreased its execution time by
45% when switching to this protocol checker instead.
Compared to the VUnit checker, this entity is missing these features:
Reset support.
Checking for undefined bits in payload fields.
Checking that all started packets finish with a proper
last.Performance checking that
readyis asserted within a certain number of cycles.Logger support. Meaning, it is not possible to mock or disable the checks in this entity.
clean_packet_dropper.vhd
An incoming packet will be dropped cleanly if drop is asserted for at least one clock cycle
during the active packet.
Once drop has been asserted during an active packet, this entity will
Not pass anything of the current
inputpacket on to theresultside, including anything that was consumed beforedropwas asserted.This means that only whole, non-corrupted, packets will be available on the
resultside.Keep
input_readyhigh until the whole packet has been consumed, so the upstream on theinputside is not stalled.
Note
The fifo.vhd instance in this module is in packet mode, meaning that a whole packet
has to be written to FIFO before any data is passed on to result side.
Hence the fifo_depth generic has to be chosen so that it can hold the maximum possible
packet length from the input side.
clock_counter.vhd
Measure the switching rate of an unknown clock by using a free-running reference clock of known frequency.
Note
This entity instantiates a resync_counter.vhd block. See documentation of that entity for constraining details.
The frequency of target_clock is given by
target_tick_count * reference_clock_frequency / 2 ** resolution_bits
The target_tick_count value is updated every 2 ** resolution_bits cycles.
It is invalid for 2 * 2 ** resolution_bits cycles in the beginning as reference_clock
starts switching, but after that it is always valid.
For the calculation to work, target_clock must be no more than
2 ** (max_relation_bits - 1) times faster than reference_clock.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
SRLs |
FFs |
|---|---|---|---|
resolution_bits = 24 max_relation_bits = 6 |
84 |
5 |
185 |
resolution_bits = 10 max_relation_bits = 4 |
38 |
2 |
86 |
common_context.vhd
A VHDL context for including the packages in this library.
common_pkg.vhd
Package with common features that do not fit in anywhere else, and are not significant enough to warrant their own package.
debounce.vhd
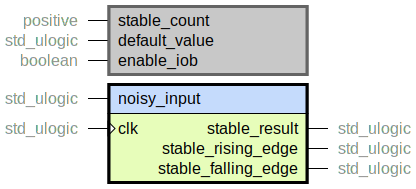
Simple debounce mechanism to be used with asynchronous FPGA input pins. E.g. the signal from a button or dip switch. It eliminates noise, glitches and metastability by requiring the input to have a stable value for a specified number of clock cycles before propagating the value.
event_aggregator.vhd
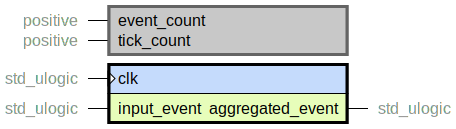
Aggregate events/pulses so that aggregated_event happens more sparsely than
input_event.
This is commonly used in an interrupt-based system control flow to avoid bogging
down the CPU with too many interrupts.
It is suitable in situations where knowledge of whether something has occurred is more important
than the exact number of times it occurred.
An input_event will always trigger an eventual aggregated_event, but the information
of how many input_event pulses have been received is lost.
Event count mechanism details
The event_count mechanism sends out an aggregated_event pulse after a certain number of
input_event pulses have been received.
Tick count mechanism details
The tick_count mechanism periodically sends out an aggregated_event pulse at a specified
interval, provided that at least one input_event pulse has been received
during the interval.
Combination
The two mechanisms can be combined, in which case the aggregated_event pulse is sent out
after either condition is met.
Either condition being met resets the counter for the other condition.
This is the most common mode of usage, since it makes sure that events are never too delayed
and never too piled up.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
FFs |
Maximum logic level |
|---|---|---|---|
event_count = 1024 tick_count = 1 |
8 |
11 |
3 |
event_count = 1 tick_count = 200000 |
10 |
20 |
6 |
event_count = 700 tick_count = 150000 |
17 |
30 |
6 |
handshake_merger.vhd
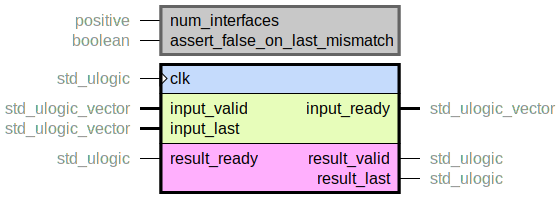
Combinatorially merge multiple AXI-Stream-like handshake interfaces into one.
The handling of data and other auxiliary signals must be performed outside of this entity.
This entity guarantees that when result_valid is asserted, the data associated with
all inputs is valid and can be used combinatorially on the result side.
If no interface is stalling, then full throughput is sustained through this entity.
handshake_mux.vhd
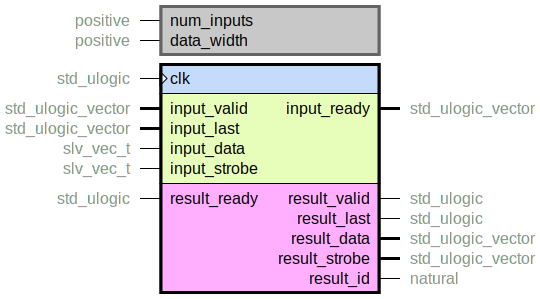
Multiplex between many AXI-Stream-like inputs towards one output bus.
Will lock onto one input and let its data through until a packet has passed, as indicated
by the last signal.
The implementation is simple, which comes with a few limitations:
Warning
If there are holes in an input packet stream after valid has been asserted, this
multiplexer will be unnecessarily stalled even if another input has data available.
It is up to the user to make sure that this does not occur, using e.g. a fifo.vhd
in packet mode, or calculate that the system throughput is still sufficient.
The arbitration is done in the simplest most resource-efficient manner possible, which
means that one input can block others if it continuously sends data.
handshake_pipeline.vhd
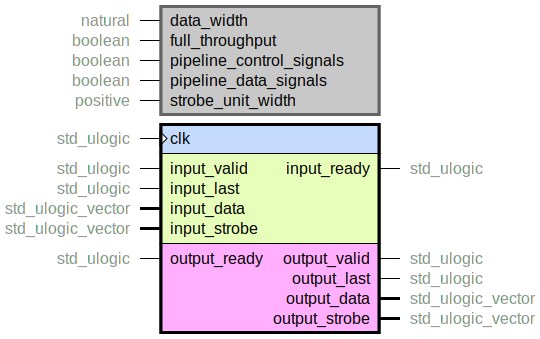
Handshake pipeline. Is used to ease the timing of a streaming data interface by inserting register stages on the data and/or control signals.
There are many modes available, with different characteristics, that are enabled
with different combinations of full_throughput, pipeline_control_signals
and pipeline_data_signals.
See the descriptions within the code for more details about throughput and fanout.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
FFs |
Maximum logic level |
|---|---|---|---|
data_width = 32 full_throughput = True pipeline_control_signals = True pipeline_data_signals = True |
41 |
78 |
2 |
data_width = 32 full_throughput = True pipeline_control_signals = False pipeline_data_signals = True |
1 |
38 |
2 |
data_width = 32 full_throughput = True pipeline_control_signals = False pipeline_data_signals = False |
0 |
0 |
0 |
data_width = 32 full_throughput = False pipeline_control_signals = True pipeline_data_signals = True |
1 |
39 |
2 |
data_width = 32 full_throughput = False pipeline_control_signals = True pipeline_data_signals = False |
2 |
3 |
2 |
data_width = 32 full_throughput = False pipeline_control_signals = False pipeline_data_signals = True |
2 |
38 |
2 |
data_width = 32 full_throughput = False pipeline_control_signals = False pipeline_data_signals = False |
0 |
0 |
0 |
handshake_splitter.vhd
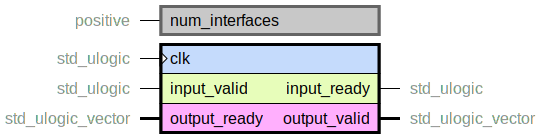
Combinatorially split an AXI-Stream-like handshaking interface, for cases where many slaves
are to receive the data.
Maintains full throughput and is AXI-stream compliant in its handling of the handshake signals
(valid does not wait for ready, valid does not fall unless a transaction
has occurred).
This entity has no pipelining of the handshake signals, but instead connects
them combinatorially.
This increases the logic depth for handshake signals where this entity is used.
If timing issues occur (on the input or one of the output s) a
handshake_pipeline.vhd instance can be used.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
FFs |
|---|---|---|
num_interfaces = 2 |
4 |
2 |
num_interfaces = 4 |
9 |
4 |
keep_remover.vhd
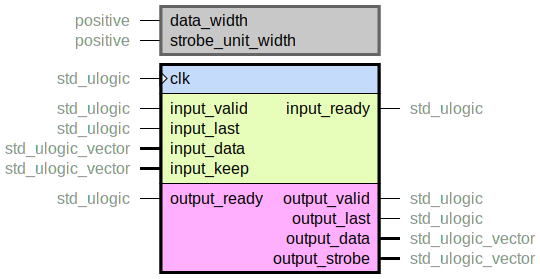
This entity removes strobe’d out lanes from the input, resulting in an output stream where all lanes are always strobed (except for the last beat, potentially). The strobe on input can be considered as the TKEEP signal in AXI-Stream terminology, and the output strobe would be TKEEP/TSTRB.
The entity works by continuously filling up a data buffer with data from the input.
Only the lanes that are strobed will be saved to the buffer.
Note that input words may have all their lanes strobed out (except for the last beat, see below).
When enough lanes are saved to fill a whole word, data is passed to the output by asserting
output_valid. When input_last is asserted for an input
word, an output word will be sent out, with output_last asserted, even if a whole strobed
word is not currently filled in the buffer.
The strobe unit data width is configurable via a generic. Most of the time it would be eight, i.e. a byte strobe. But in some cases the strobe represents a wider quanta, in which case the generic can be increased. Increasing the generic will drastically decrease the resource utilization, since that is the “atom” of data that is handled internally.
The handling of input_last presents a corner case.
Lets assume that data_width is 16 and strobe_unit_width is 8.
Furthermore, there is one atom of data available in the buffer, and input stream has both lanes
strobed. In this case, one input word shall result in two output words. The first output word
comes from a whole word being filled in the buffer. The second word comes from a half filled word
in the buffer, but input_last being asserted.
This is solved by having a small state machine that pads input data with an extra word when
this corner case arises. The padding stage makes it possible to have a very simple data buffer
stage, with low resource utilization.
Throughput
The entity achieves full throughput, except for the corner case mentioned above, where it might stall one cycle on the input.
Limitations
input_lastmay not be asserted on an input word that has all lanes strobed out.There may never be a ‘1’ above a ‘0’ in the input strobe. E.g. “0111” is allowed, but “1100” is not.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
FFs |
DSP Blocks |
Maximum logic level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
data_width = 32 strobe_unit_width = 16 |
88 |
79 |
0 |
3 |
data_width = 64 strobe_unit_width = 8 |
410 |
175 |
0 |
6 |
data_width = 128 strobe_unit_width = 32 |
414 |
282 |
0 |
5 |
periodic_pulser.vhd
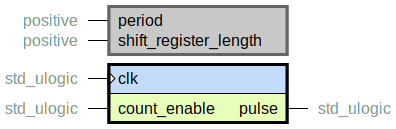
Outputs a one cycle pulse after a generic number of assertions of count_enable.
Shift registers are used as far as possible to create the pulse. This makes the implementation resource efficient on devices with cheap shift registers (such as SRLs in Xilinx/AMD devices). In the worst case a single counter is created.
The period is broken down into factors that are represented using shift
registers, with the shift register length being the factor value. By rotating the shift register
on each count_enable, a fixed period is created.
When possible, multiple shift registers are AND-gated to create a longer
period. For example a period of 30 can be achieved by gating two registers of length 10
and 3. This method only works if the lengths are mutual primes (i.e. the greatest common
divisor is 1).
If the remaining factor is not 1 after the shift registers have been added, a new instance of this module is added through recursion.
If period cannot be factorized into one or more shift registers, recursion ends with
either a simple counter or a longer shift register (depending on the size of the factor).
Example
Let’s say that the maximum shift register length is 16. A period of 510 = 10 * 3 * 17 can then be achieved using two shift registers of length 10 and 3, and then instantiating a new periodic_pulser.vhd
[0][0][0][0][0][0][0][0][0][1]
\
[AND] -> pulse -> [periodic_pulser with period 17]
/
[0][0][1]
The next stage will create a counter, because 17 is a prime larger than the maximum shift register length.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
SRLs |
FFs |
|---|---|---|---|
period = 33 shift_register_length = 33 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
period = 33 shift_register_length = 1 |
6 |
0 |
6 |
period = 37 shift_register_length = 33 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
period = 37 shift_register_length = 1 |
6 |
0 |
6 |
period = 100 shift_register_length = 33 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
period = 100 shift_register_length = 1 |
8 |
0 |
7 |
period = 125 shift_register_length = 33 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
period = 125 shift_register_length = 1 |
7 |
0 |
7 |
period = 127 shift_register_length = 33 |
5 |
4 |
1 |
period = 127 shift_register_length = 1 |
8 |
0 |
7 |
period = 4625 shift_register_length = 33 |
7 |
4 |
3 |
period = 4625 shift_register_length = 1 |
2 |
0 |
13 |
period = 311000000 shift_register_length = 33 |
15 |
4 |
15 |
period = 311000000 shift_register_length = 1 |
2 |
0 |
29 |
strobe_on_last.vhd
The goal of this entity is to process an AXI-Stream so that packets where last is asserted on
a word that is completely strobed out are modified so that last is instead asserted on the
last word which does have a strobe.
As a consequence of this, all words in the stream that are completely strobed out are dropped by this entity.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
FFs |
Maximum logic level |
|---|---|---|---|
data_width = 8 |
7 |
12 |
3 |
data_width = 32 |
8 |
39 |
3 |
data_width = 64 |
9 |
75 |
3 |
time_pkg.vhd
Contains a couple of methods for working with the VHDL time type.
The time type can be tricky sometimes because its precision is implementation dependent,
just like the integer and universal_integer types:
integer'high is
2147483647 in GHDL 3.0.0-dev, corresponding to a 32 bit signed integer.
2147483647 in Vivado 2021.2, corresponding to a 32 bit signed integer.
time'high is
9223372036854775807 fs in GHDL 3.0.0-dev, corresponding to a 64 bit signed integer. Time values greater than this will result in an error.
2147483647 fs in Vivado 2021.2, corresponding to a 32 bit signed integer. However, Vivado 2021.2 can represent time values greater than this since it uses a dynamic secondary unit for
time, as outlined in IEEE Std 1076-2008, page 39. Precision is never greater than 32 bits though.
In the standard library, the following functions are available for working with
time values (IEEE Std 1076-2008, page 260):
function "=" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return BOOLEAN;
function "/=" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return BOOLEAN;
function "<" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return BOOLEAN;
function "<=" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return BOOLEAN;
function ">" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return BOOLEAN;
function ">=" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return BOOLEAN;
function "+" (anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "- (anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "abs" (anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "+" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "-" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "*" (anonymous: TIME; anonymous: INTEGER) return TIME;
function "*" (anonymous: TIME; anonymous: REAL) return TIME;
function "*" (anonymous: INTEGER; anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "*" (anonymous: REAL; anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "/" (anonymous: TIME; anonymous: INTEGER) return TIME;
function "/" (anonymous: TIME; anonymous: REAL) return TIME;
function "/" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return universal_integer;
function "mod" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function "rem" (anonymous, anonymous: TIME) return TIME;
function MINIMUM (L, R: TIME) return TIME;
function MAXIMUM (L, R: TIME) return TIME;
Notably missing is a convenient and accurate way of converting a time value to real
or integer.
So that is most of the complexity in the conversion functions below.
types_pkg.vhd
Some basic types that make it easier to work with VHDL. Also some basic functions operating on these types.
width_conversion.vhd
Width conversion of an AXI-Stream-like data bus. Can handle downsizing (wide to thin) or upsizing (thin to wide). The data widths must be a power-of-two multiple of each other. E.g. 10->40 is supported while 8->24 is not.
There is a generic to enable usage of the last signal. The last indicator will be passed
along with the data from the input to output side as-is. Note that enabling the
support_unaligned_packet_length generic will enable further processing of last, but in
barebone configuration the signal is merely passed on.
There is a generic to enable strobing of data. The strobe will be passed on from
input to output side as-is. Note that enabling support_unaligned_packet_length
generic will enable further processing of strobe, but in barebone configuration the signal
is merely passed on.
This means, for example, that there might be output words where all strobe lanes are
zero when downsizing.
There are some limitations, and possible remedies, concerning packet length alignment, depending on if we are doing upsizing or downsizing. See below.
Downsizing behavior
When doing downsizing, one input beat will result in two or more output beats, depending
on width configuration. This means that the output packet length is always aligned with the input
data width. This is not always desirable when working with the strobe and last signals.
Say for example that we are converting a bus from 16 to 8, and input_last is asserted on a
beat where the lowest byte is strobed but the highest is not. In this case, we would want
output_last to be asserted on the second to last byte, and the last byte (which is strobed
out) to be removed.
This is achieved by enabling the support_unaligned_packet_length generic.
If the generic is not set, output_last will be asserted on the very last byte, which will
be strobed out.
Upsizing behavior
When upsizing, two or more input beats result in one output beat, depending on width
configuration. This means that the input packet length must be aligned with the output
data width, so that each packet fills up a whole number of output words.
If this can not be guaranteed, then the support_unaligned_packet_length mode can be used.
When that is enabled, the input stream will be padded upon last indication so that a whole
output word is filled.
Consider the example of converting a bus from 8 to 16, and input last is asserted on the
third input beat. If support_unaligned_packet_length is disabled, there will be one output
beat sent and half an output beat left in the converter.
If the mode is enabled however, the input stream will be padded with another byte so that an
output beat can be sent. The padded parts will have strobe set to zero.
Note that the handling of unaligned packet lengths is highly dependent on the input stream being well behaved. Specifically
There may never be input beats where
input_strobeis all zeros.For all beats except the one where
input_lastis asserted,input_strobemust be asserted on all lanes.There may never be a
'1'above a'0'in theinput_strobe.
User signalling
By setting the user_width generic to a non-zero value, the input_user port can be used
to pass auxiliary data along the bus.
When downsizing, i.e. when one input beat results in multiple output beats, the
output_user port will have the same width as the input_user port.
Each output beat will have the same user value as the input beat that created it.
When upsizing, i.e. when multiple input beats result in one output beat, the output_user
port will have the same width as the input_user port multiplied by the conversion factor.
The output_user port will have the concatenated input_user values from all the input
beats that created the output beat.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_common.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
FFs |
Maximum logic level |
|---|---|---|---|
input_width = 32 output_width = 16 enable_last = False enable_strobe = False user_width = 0 support_unaligned_packet_length = False |
20 |
51 |
2 |
input_width = 32 output_width = 16 enable_last = True enable_strobe = True user_width = 0 support_unaligned_packet_length = False |
23 |
59 |
2 |
input_width = 32 output_width = 16 enable_last = True enable_strobe = True user_width = 0 support_unaligned_packet_length = True |
27 |
60 |
3 |
input_width = 32 output_width = 16 enable_last = True enable_strobe = True user_width = 5 support_unaligned_packet_length = True |
32 |
70 |
3 |
input_width = 16 output_width = 32 enable_last = False enable_strobe = False user_width = 0 support_unaligned_packet_length = False |
35 |
51 |
2 |
input_width = 16 output_width = 32 enable_last = True enable_strobe = True user_width = 0 support_unaligned_packet_length = False |
40 |
59 |
2 |
input_width = 16 output_width = 32 enable_last = True enable_strobe = True user_width = 0 support_unaligned_packet_length = True |
44 |
62 |
2 |
input_width = 16 output_width = 32 enable_last = True enable_strobe = True user_width = 5 support_unaligned_packet_length = True |
54 |
77 |
2 |
width_conversion_pkg.vhd
Package with functions for width_conversion.vhd.