Module math
This document contains technical documentation for the math module.
To browse the source code, visit the repository on GitHub.
This module contains a contains entities and packages for common math operations in VHDL.
math_pkg.vhd
Package with some common mathematical functions.
saturate_signed.vhd
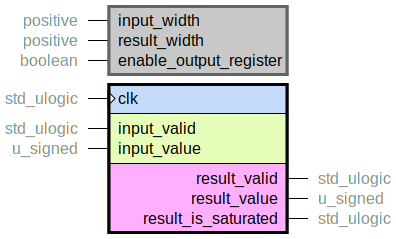
Saturate a signed number by removing MSBs. Typically used in fixed-point applications after performing arithmetic operations, such as addition or multiplication. Or to clamp a value from a third source to a certain range.
In digital arithmetic scenarios, the concept of guard bits is commonly used, and the input value will be of the form:
input_value = S G G G N N N N N N N N
Where S is the sign bit, and G are a guard bits.
Note that the number of guard bits, three in the example above, is the difference between
input_width and result_width.
Pseudo code
This entity performs the following operation, which is equivalent to a range clamping with power-of-two limits:
min_value = - 2 ** (result_width - 1)
max_value = 2 ** (result_width - 1) - 1
if input_value < min_value:
return min_value
if input_value > max_value:
return max_value
return input_value
Fixed-point implementation
The pseudo code above is efficiently implemented in digital logic by looking at the guard bits and the sign bit. If any of them have different value, the input value is outside the result range. If the sign bit is ‘1’, the input is negative, and the result should be greatest negative value possible. If the sign bit is ‘0’, the input is positive, and the result should be the greatest positive value possible.
Note that you have to choose your number of guard bits carefully in any upstream arithmetic operation. If you have too few guard bits, the value might already have wrapped around, and the saturation will not work as expected. This is all dependent on the details of your application.
truncate_round_signed.vhd
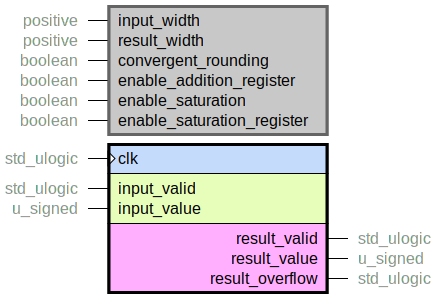
Truncate a numeric value by removing LSBs and rounding the result.
Rounding details
The truncation can be seen as removing a number of fractional bits from a fixed-point number. The result value will be the closest integer value to the fractional input value. If the value is exactly in the middle between two integers, the result will be
The integer value of the two that is even, if
convergent_roundingis true.The integer value of the two that is closest to positive infinity, if
convergent_roundingis false.
Convergent rounding is the default rounding mode used in IEEE 754 and comes with some advantages, most notably that it yields no bias. Convergent mode does consume one more LUT and results in a longer critical path.
Overflow and saturation
If the input value is already at the maximum value, and the fractional value is such that a
rounding upwards should happen, the addition will overflow and the result_overflow signal
will read as 1.
If the enable_saturation generic is set to true, the result will instead be saturated to the
maximum value.
Alternative approach
One could sign-extend the input value with one guard bit, add then instantiate saturate_signed.vhd on the result. The netlist build showed, however, that this alternative approach results in more LUTs and longer critical path, for both wide and narrow words.
Resource utilization
This entity has netlist builds set up with automatic size checkers in module_math.py. The following table lists the resource utilization for the entity, depending on generic configuration.
Generics |
Total LUTs |
FFs |
Maximum logic level |
|---|---|---|---|
convergent_rounding = False enable_addition_register = True enable_saturation = True enable_saturation_register = True input_width = 32 result_width = 24 |
6 |
52 |
6 |
convergent_rounding = True enable_addition_register = True enable_saturation = True enable_saturation_register = True input_width = 32 result_width = 24 |
7 |
52 |
8 |
unsigned_divider.vhd
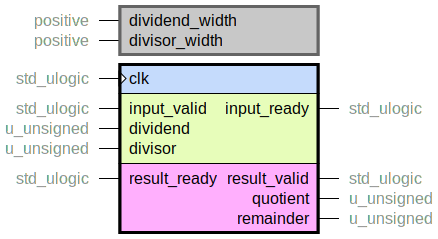
Calculates
dividend / divisor = quotient + remainder / divisor
This is a bit serial divider.
Algorithm is the same as long division from elementary school, but with number base two.
Latency scales linearly with dividend_width.